Search Results for: rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The rough endoplasmic reticulum (rough ER or rER) is a membrane-bound organelle... Read More
Endoplasmic reticulum
Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition The endoplasmic reticulum is a membrane-bound organelle in cells of eukaryotic cells... Read More
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum Definition Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (sER) is part of or a region in the endoplasmic... Read More
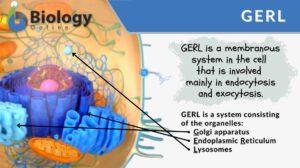
Endomembrane system
Ever wondered how biomolecules are made within the cell and then they are released outside the cell for use by the body?... Read More
Golgi apparatus
Golgi Apparatus Definition The Golgi apparatus is a membrane-bound organelle in eukaryotic cells. It plays a crucial role... Read More
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Definition noun plural: sarcoplasmic reticula (cell biology) The special type of smooth endoplasmic reticulum found in... Read More
Eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic Cells Definition What is a eukaryotic cell? Eukaryotic cells refer to the cells of (or derived from) eukaryotes,... Read More
Role of Golgi Apparatus & Endoplasmic Reticulum in Protein Synthesis
Continued from the previous tutorial that introduces protein synthesis... mRNA and tRNA mRNA leaves the nucleus and enters... Read More
Cell Structure
The interior of human cells is divided into the nucleus and the cytoplasm. The nucleus is a spherical or oval-shaped... Read More
Fibroblast
The building block of living things is known as the cell. The cell contributes to many parts and functions of different... Read More
Plant Cells vs. Animal Cells
Plant Cells Most cells are not visible with the naked eye. However, with microscopes of various types, plant cells can be... Read More
Glycosylation
Definition noun A biochemical process where a glycan attaches to a protein, a lipid, or other organic molecule, especially... Read More
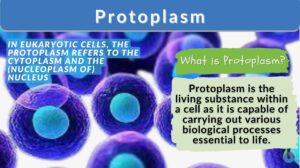
Protoplasm
Protoplasm Definition The protoplasm is regarded as "the living material or the living content of a cell". It is fluid... Read More
Elaioplast
Definition noun, plural: elaioplasts (botany) A leucoplast that stores oil Supplement Plastids are organelles involved in... Read More
Protein Synthesis
If you have jumped straight to this page, you may wish to look at the previous tutorial about DNA, which gives background... Read More
Animal cell
An animal cell is the fundamental functional unit of life of animals. It is also the basic unit of reproduction. Animal... Read More
Polypeptide
Polypeptide Definition Biology What are polypeptides? A polypeptide is defined as a polymer of amino acids joined together... Read More
Signal recognition particle
Definition noun A protein-RNA complex important in binding to the mRNA for the recognition of signal peptide on a nascent... Read More
Provacuole
provacuole (Science: plant biology) In plant cells provacuoles are budded directly from the rough endoplasmic reticulum and... Read More
Proteoglycan
What are proteoglycans? Proteoglycans are primarily a type of polysaccharide. Structurally, proteoglycans are... Read More
Lysosomal enzyme
Definition noun plural: lysosomal enzymes ly·so·somal en·zyme, ˈlaɪsəˌsoʊm əl ˈɛnzaɪm (biochemistry) Any of... Read More
Dohle body
Definition noun, plural: Dohle bodies Round or oval cytoplasmic inclusion of neutrophils containing remnants of rough... Read More
Plasma B cell
Definition noun, plural: plasma B cells A large B lymphocyte that when exposed to antigen, produce, and secrete large... Read More
Hepatocyte
Definition noun, plural: hepatocytes Any of the large, polygonal-shaped cells in the liver. Supplement Hepatocytes are the... Read More